Saltmarsh Snake
- Scientific Name
- Nerodia clarkii
- Also Known As
- Saltmarsh Snake
- Range
- The Coasts of Florida
- Diet
- Fish
- Life Expectancy
- 9 Years
Quick Links
Saltmarsh Snakes in Central Florida
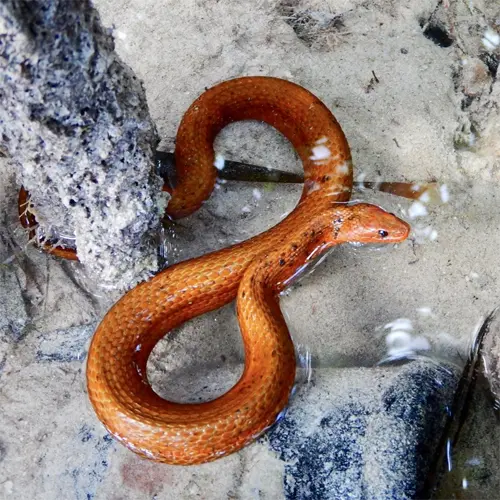
The saltmarsh snake (Nerodia clarkii) is a semiaquatic colubrid species that inhabits coastal wetlands and marshy areas of the southeastern United States. In Florida, saltmarsh snakes are found along both the Gulf and Atlantic coasts.
This article provides detailed identification tips, biology facts, and information on saltmarsh snake habits and distribution within central Florida.
Saltmarsh Snake Subspecies in Central Florida
Mangrove Saltmarsh Snake
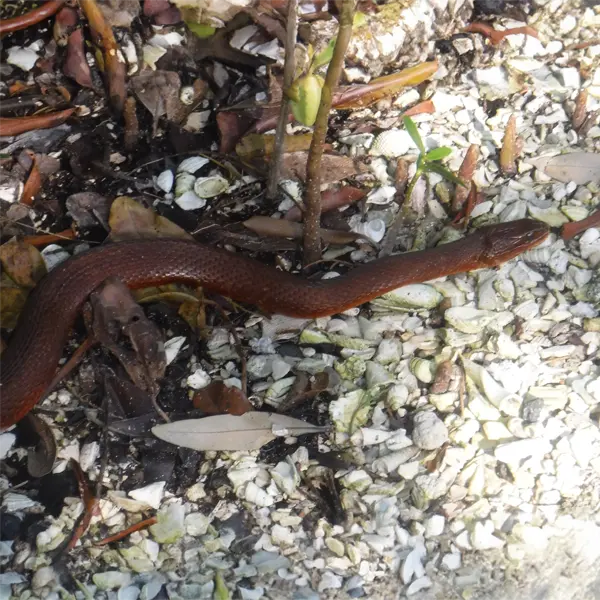
The mangrove saltmarsh snake (Nerodia clarkii ssp. compressicauda) is a special subspecies of the saltmarsh snake found only in mangrove swamps along the southern Florida coast. Genetic testing shows the mangrove snakes are isolated and have evolved differently, which is why they are considered a separate subspecies.
Mangrove saltmarsh snakes are smaller, around 20-28 inches long, compared to their northern relatives. They also have a darker color and more strongly ridged scales. Living only in mangroves, their smaller size and different scales seem adapted to that habitat.
Protecting the fragile mangrove ecosystems is crucial for the mangrove snake’s survival, since they are already declining from wetland loss. Calling them a distinct subspecies highlights the need to protect their mangrove home in southern Florida.
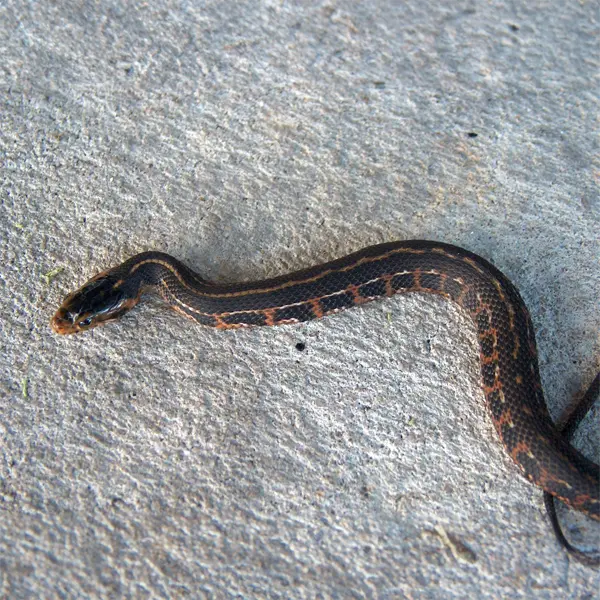

Atlantic Saltmarsh Snake
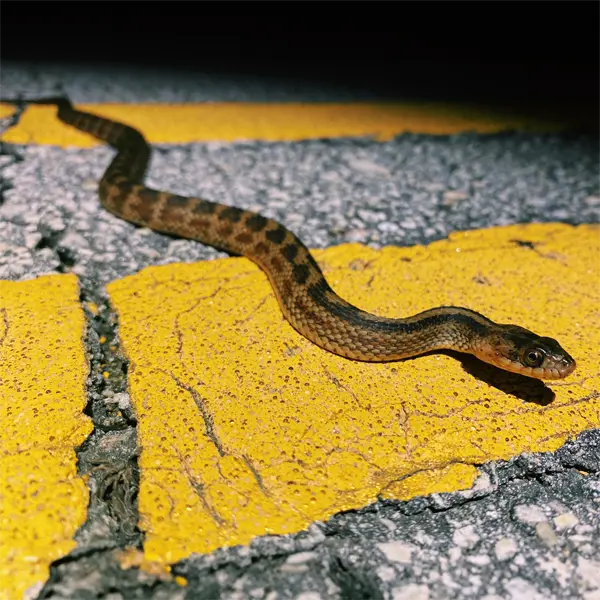
The Atlantic saltmarsh snake (Nerodia clarkii ssp. taeniata) is another subspecies of the saltmarsh snake found along the Atlantic coast and inland wetlands. Genetic evidence indicates Atlantic saltmarsh snakes split off long ago from other populations.
They prefer freshwater habitats over saltwater marshes. Atlantic saltmarsh snakes grow over 3 feet long and have weak lateral blotches compared to other subspecies. They also have a lighter color that blends into grassy marshes.
The Atlantic subspecies is adapted to hunting in vegetated freshwater wetlands versus muddy salt flats. Loss of inland wetlands has reduced their numbers.
Appearance and Identification
The Saltmarsh Snake can be distinguished from look-alike species by the following characteristics
Saltmarsh snakes can be confused with the closely related Atlantic saltmarsh snake (N. fasciata). However, N. clarkii has more pronounced lateral blotches and prefers coastal saltwater habitats over freshwater wetlands.
Maturation Rate
Saltmarsh snakes grow quickly. Hatchlings double in size within their first year, reaching adult length by age 2-3. Males tend to mature slightly faster than females. Rapid growth allows saltmarsh snakes to take advantage of the seasonal abundance of fish, their primary food source.
Habits and Behavior
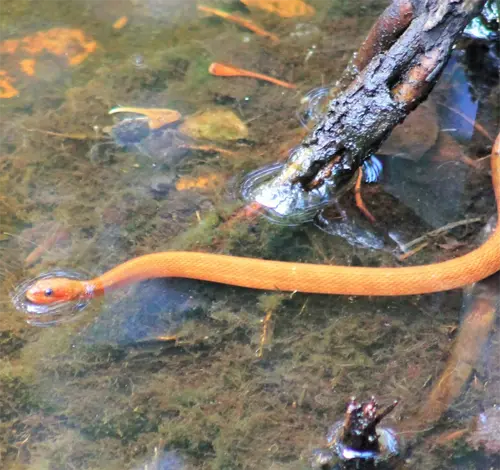
Saltmarsh snakes are active during the day, especially when tide levels allow access to prey. They spend much of their time partially submerged in shallow water searching for food. Saltmarsh snakes are excellent swimmers but prefer shallows where they can keep most of their body anchored to the bottom.
Saltmarsh snakes often bask on marsh grass during high tides. If threatened on land, they will quickly retreat to the water. They may strike or release a foul musk as defense before fleeing. Saltmarsh snakes often anchor their body with their tail wrapped around grass blades and floating debris while their head remains underwater scanning for prey.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Saltmarsh snakes reach breeding maturity around 2-3 years old. Mating occurs in the spring after emergence from winter dormancy. Females lay 5-20 eggs in June or July in a moist, hidden site, often under debris or dense vegetation. The eggs hatch in late summer to early fall. Hatchlings grow rapidly and are independent immediately.
Saltmarsh snakes may live up to 9 years in the wild. Their cryptic habits make estimating longevity challenging.
Ideal Habitat and Range
Central Florida’s extensive coastline and shallow estuaries provide ideal saltmarsh snake habitat. Average annual rainfall ranges from 45 inches (1143 mm) along the Gulf coast to over 60 inches (1524 mm) on the Atlantic side. Hot, humid summer weather fuels rapid plant growth.
Extensive salt marsh stretches along the Gulf coast around Crystal River and Homosassa. Mangrove swamps also harbor populations. On the Atlantic coast, Canaveral National Seashore and Merritt Island preserve vast saltwater marshes, tidal flats, and scrub critical for the snakes.
Urban development has reduced saltmarsh snake habitat in central Florida. However, conservation efforts protect remaining coastal wetlands. Early drainage and impoundment especially diminished marshes along the Gulf coast. Ongoing restoration aims to reestablish tidal flow and natural salinity levels to benefit marsh fauna including the saltmarsh snake.
Diet and Feeding
Fish comprise over 90% of the saltmarsh snake’s diet. They prey heavily on Fundulus killifish, Cyprinodon minnows, and Poecilia mollies. Eels, shrimp, crabs, and frogs are also occasionally eaten. Juveniles start on fish larvae, shrimp and other small invertebrates.
Saltmarsh snakes locate prey by sight and sense vibrations through their jaw bones resting on the substrate. They swallow fish head first underwater. For larger prey, they may haul themselves partially ashore to maneuver the meal. Saltmarsh snakes may ingest fish up to 1/3 of their own body length. They can go weeks between major feedings.

Photo 9367236 © mikeakresh, CC BY-NC

Common Health Risks
Saltmarsh snakes are non-venomous and generally not aggressive. They prefer retreat over confrontation. Bites mainly occur due to accidental handling and are very rare. Despite lacking venom, their saliva contains bacteria that pose a mild infection risk if bitten.
A greater hazard is driving vehicles over snakes basking on warm roads, though saltmarsh snakes tend to remain near water. Overall, saltmarsh snakes pose minimal risks to humans and pets if left undisturbed. Their importance controlling insect and rodent pest species far outweighs any dangers.
Preventing Saltmarsh Snake Conflicts
The cryptic nature of saltmarsh snakes makes encounters infrequent. Give snakes space and do not attempt to handle or harm them. Supervise children and pets near salt marshes. Avoid driving along marsh roads at low tide when snakes may be exposed.
Snakes that enter yards or structures likely emerged from flooded burrows. Monitor for points of entry after major storms or unusually high tides. Sealing any openings at least 1/4 inch wide will exclude snakes long-term. Traps can remove strays until permanent exclusion is implemented.
Saltmarsh Snakes in Central Florida – Conclusion
Saltmarsh snakes are elusive but ecologically vital inhabitants of Florida’s threatened coastal wetlands. While human expansion has reduced populations, restoration efforts aim to preserve saltmarsh habitats critical for their survival.
By respecting saltmarsh snakes’ space and sealing routes into buildings, conflicts can be avoided. Ultimately, maintaining healthy coastal ecosystems allows saltmarsh snakes and humans to safely coexist along central Florida’s scenic coasts.