Round-tailed Muskrat (Florida Water Rat) in Central Florida
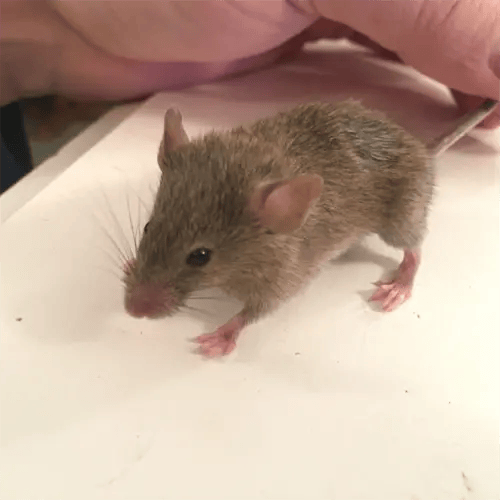
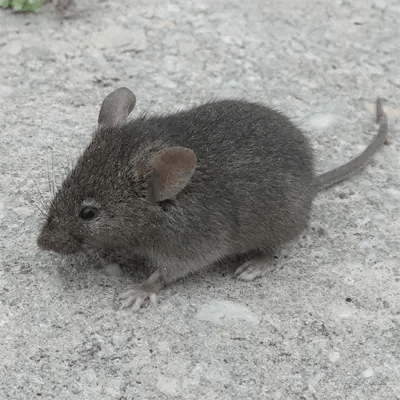
The house mouse (Mus musculus) is a small, prolific rodent that thrives in and around homes and buildings.
House mice pose significant economic and health risks if populations are not well-controlled. This guide covers house mouse identification, biology, behavior, health hazards, and prevention methods relevant to central Florida.
Appearance and Identification
House mice have characteristic features that distinguish them from other small rodents
Mature house mice are smaller with larger ears and eyes compared to rats. Their feet lack the rat’s long toes adapted for climbing and burrowing. House mice vocalizations are higher-pitched squeaks compared to the rumbling noises rats make.
Maturation Rate
Newborn pups are hairless, blind and dependent on the mother. They develop fur at 1 week and open their eyes at 2 weeks old. Weaning occurs by 3-4 weeks old as they transition to solid food. House mice reach reproductive maturity and near-adult size by 6 weeks old. They are independent at 4-5 weeks old.
Habits and Behavior
House mice are nocturnal but may venture out during the day if hungry. They have poor eyesight but keen senses of smell, taste, hearing, and touch. House mice are wary, nibbling small samples of new foods before eating more.
House mice are agile climbers and can walk up vertical surfaces but prefer horizontal movement. They can jump up to 12 inches (30 cm) high and survive falls from great heights uninjured. House mice can squeeze through very small spaces and openings just 1/4 inch (6 mm) wide.
They tend to forage within a 30 foot (10 m) radius of their nesting area. House mice are curious but avoid novel spaces and objects at first. Given time, they gradually habituate and explore new additions in their territory. House mice constantly explore and map out their surroundings.
Reproduction and Lifespan
House mice are fast maturing and prolific breeders. Females can start breeding as early as 6 weeks old and bear 5-10 litters per year. Litter sizes range from 4-12 young with a 21 day gestation period.
The average lifespan is just 9-12 months but house mice numbers rebound quickly after declines due to their high reproductive capacity. Females can conceive again within days after giving birth.
Ideal Habitat and Range
Central Florida’s warm, humid climate with abundant vegetation and agricultural activity provides ideal habitat for house mice populations to thrive year-round. Average temperatures range from the low 70s F (22C) to upper 70s F (25C). Rainfall exceeds 50 inches (1270 mm) annually.
Rural forests, wetlands, citrus groves, vegetable farms, and pastures provide an ample food supply and harborage sites. Developed areas offer shelter inside homes, garages, sheds, and access to pet food, garbage, and pantry items. Open buildings and gaps allow entry while insulation and clutter offer nesting areas.
As rapid breeders, house mice numbers can quickly rise to infestation levels under favorable conditions. Exclusion and population control is required to prevent destructive house mice colonies from becoming established in and around structures.
Diet and Feeding
House mice are omnivorous generalists, consuming a wide variety of plant and animal matter. Their daily food intake equals about 1/10 of their body weight. House mice need a water source if sufficient moisture isn’t obtained from food.
Typical food sources include:
- Grains – cereal, rice, pasta, etc.
- Fruit and veggies – berries, greens, root vegetables.
- Nuts and seeds – sunflower, peanuts, almonds.
- Insects – beetles, caterpillars, cockroaches.
- Fungi and lichens.
- Leftover human food, crumbs.
- Pantry items – cereal, crackers, flour, etc.
- Pet food.
- Garbage scraps.
Foraging house mice leave behind feces and urine trails that other mice follow. They make 30-40 visits per day back to their nest to eat, resting in between foraging bouts. House mice must drink water daily if moisture isn’t obtained from food sources.
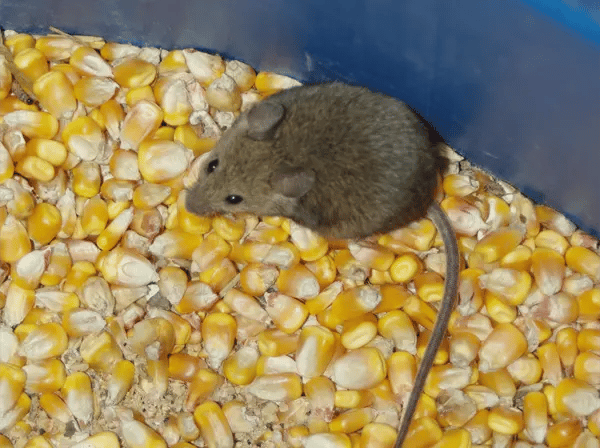


Common Health Risks
House mice can transmit over 20 different viral, bacterial, and parasitic diseases to humans, including:
- Salmonellosis – Spread through feces on surfaces. Causes diarrhea, fever, cramps.
- Leptospirosis – Spread through urine on surfaces. Causes fever, chills, vomiting.
- Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCMV) – Spread through saliva, urine, feces. Flulike illness or potentially fatal meningitis.
- Rat bite fever – Spread by infected mouse saliva from bites. Causes muscle pain, fever, headache.
House mice also trigger allergies and asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals due to debris, dander, and fecal particles they spread. Quickly addressing house mouse infestations is important to avoid associated health issues.
Preventing House Mouse Infestations
Seal all entry points into buildings with steel wool, copper mesh, caulk, concrete, or other Fill materials. Trim vegetation touching structures. Eliminate clutter and food access by storing all foodstuffs in sealed metal or glass containers.
Clean up all crumbs and spills right away. Use snap traps or live traps to remove mice. Limit openings throughout buildings to less than 1/4 inch. Inspect new objects thoroughly before bringing indoors to avoid hitchhiking mice.
With diligent exclusion and sanitation practices, house mouse invasions can be prevented. Traps and rodenticides provide additional population control when needed.

Florida Water Rats in Central Florida – Conclusion
House mice pose risks in central Florida homes, farms, and businesses due to the region’s suitable climate and abundant food supply. However, through exclusion tactics, sanitation, traps, and swift action when signs first appear, destructive house mouse colonies can be avoided.
With vigilant monitoring and integrated pest management focusing on prevention, house mice can be controlled in structures while larger populations are suppressed outdoors through habitat modification and rodenticides as needed.