Green Iguana
- Scientific Name
- Iguana iguana
- Also Known As
- American Iguana, Bamboo Chicken
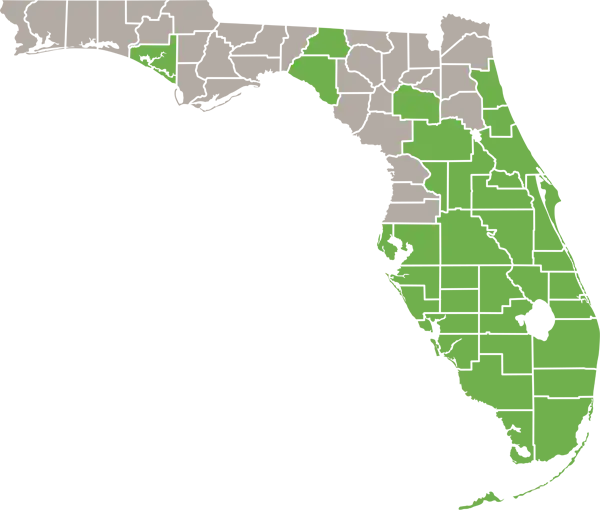
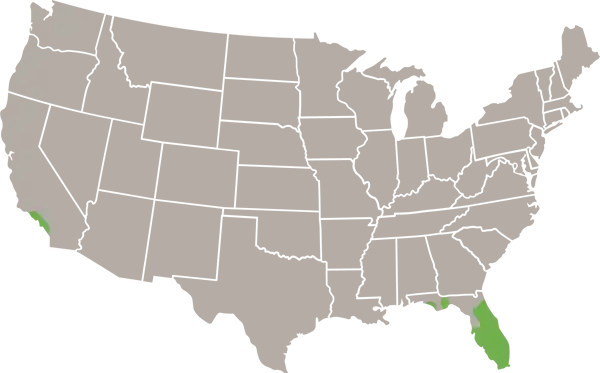
- Range
- All of Florida
- Diet
- Flowers, Leaves, Stems, and Fruit
- Life Expectancy
- 10 - 12 Years
Quick Links
Green Iguanas in Central Florida
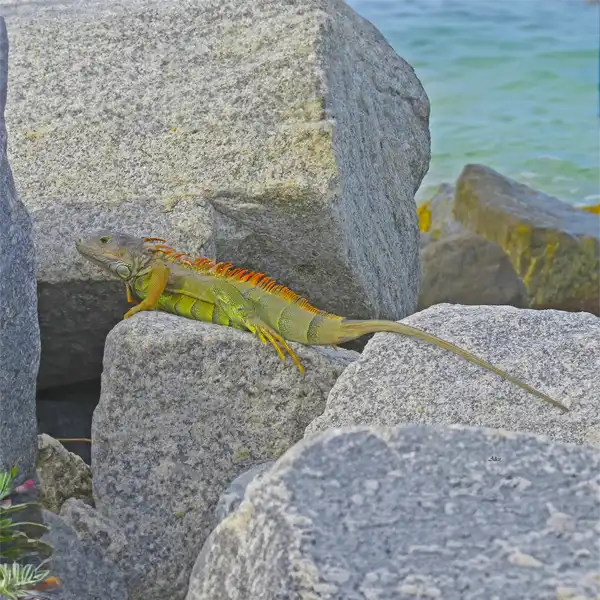
The green iguana (Iguana iguana) is a large arboreal lizard that has become an invasive pest in central Florida. Often released as unwanted pets, green iguanas thrive in the warm subtropical climate. This adaptive reptile damages infrastructure, competes with native wildlife, and can transmit salmonella to humans.
This comprehensive guide provides detailed identification tips, biology facts, and control methods for green iguanas in central Florida. Read on to learn green iguana physiology, habits, reproduction, diet, health risks, signs of infestation, and professional removal options if you have an invasive iguana problem.
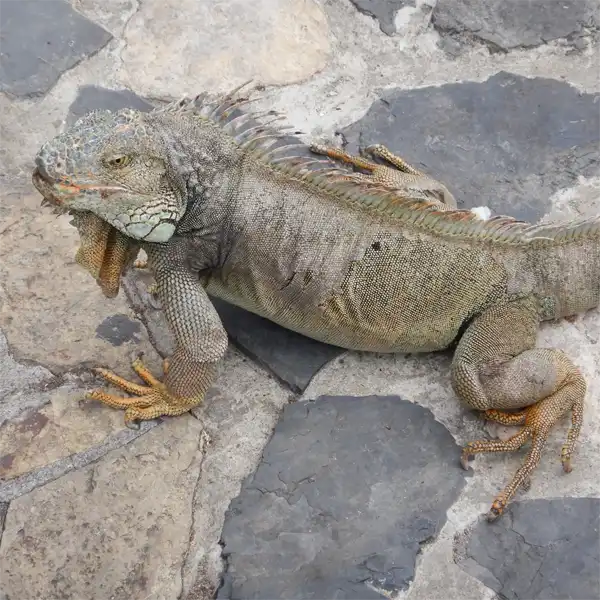
Appearance and Identification
Green iguanas can be identified by their characteristic features
Maturation Rate
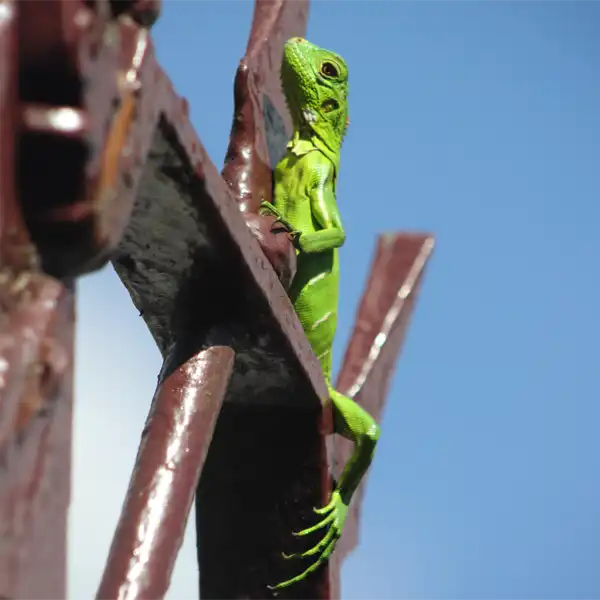
Green iguanas grow rapidly within their first 3 years, reaching full adult size. Growth slows thereafter. Sexual maturity and breeding typically occur after 2 to 4 years once they achieve substantial size.
Habits and Behavior
Green iguanas are diurnal lizards found along waterways like canals, lakes, and marshes. They bask in the sun on branches overhanging water. Excellent swimmers, they plop into water when threatened. When cold, they become lethargic and seek shelter in dense thickets or burrows. They dig burrows near water up to 15 feet (4.5 m) long.
Green iguanas are territorial, especially mature males. They are solitary except during breeding season. Males defend territory and attend communal nesting sites. Hissing, head-bobbing, and change in dewlap color are threat displays. Iguanas also inflict painful bites and scratches when cornered.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Mating takes place in late fall to early spring in Florida. Females build nests in burrows or soil and lay 20 to 60 eggs in May or June. Eggs incubate for 10 to 12 weeks. Hatchlings emerge in late summer to early fall.
Green iguanas reach maturity and begin breeding between 2 to 4 years old. Their lifespan in the wild averages 10 to 12 years but can exceed 20 years.
Ideal Habitat and Range
The climate of central Florida provides ideal conditions for breeding populations of green iguanas. Hot summer temperatures allow eggs to incubate and hatch. Warm winters sustain adult iguanas whereas prolonged cold can stress and kill them.
Plentiful waterways, marshes, and lakes provide habitat. Abundant vegetation like willows, palms, and flowering plants offer ample food. Urban heat islands allow iguanas to spread.
Diet and Feeding
Green iguanas are herbivores that occasionally eat insects and small vertebrates. Their diet consists of:
- Flowers and nectar
- Fruit – figs, mangos, grapes, berries
- Leaves and shoots
- Tree bark
Iguanas forage actively during the day, feeding on plants overhanging waterways. They consume a large amount of vegetation daily. Iguanas negatively impact orchards, gardens, and landscaping.
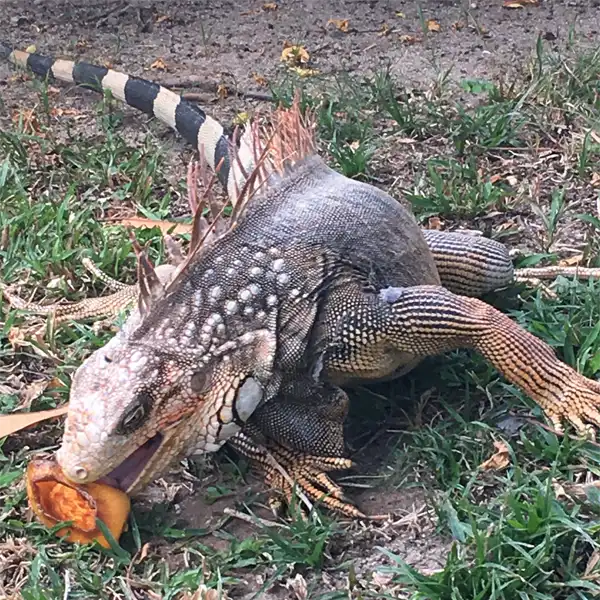

Photo 43666392 © kholovaci, CC BY-NC

Common Health Risks
Green iguanas can transmit salmonella bacteria to humans through contact with feces or contaminated water. Salmonella causes severe gastric illness with nausea, fever, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Iguanas also frequently carry ticks which are vectors for diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Bites and scratches can cause infection. Iguanas should not be kept as pets due to these health risks.
Preventing Black Spiny-tailed Iguanas
Population control through removal is crucial to curb the spread of invasive green iguanas. Traps and snares can capture iguanas for humane euthanasia. Removal of nests and eggs disrupts breeding. Hot water treatment of burrows or fumigation kills hatchlings.
Exclusion by trimming vegetation back from waterways limits basking sites. Installing barriers around sensitive gardens, orchards or pools keeps iguanas away. Discouraging illegal release as unwanted pets also prevents proliferation.
Black Spiny-tailed Iguanas in Central Florida – Conclusion
Green iguanas are a formidable invasive species in Florida’s subtropical environment. They readily spread and cause damage when unmanaged. Prevent their spread by discouraging release of pets, excluding them through vegetation control and barriers, and removing actively through trapping and nest destruction. Consistent control efforts are essential to protect wildlife, property, and public health from these harmful non-native reptiles. With vigilance and persistence, problematic green iguana populations can be contained.