The Florida Mouse
- Scientific Name
- Podomys floridanus
- Also Known As
- Florida Mouse
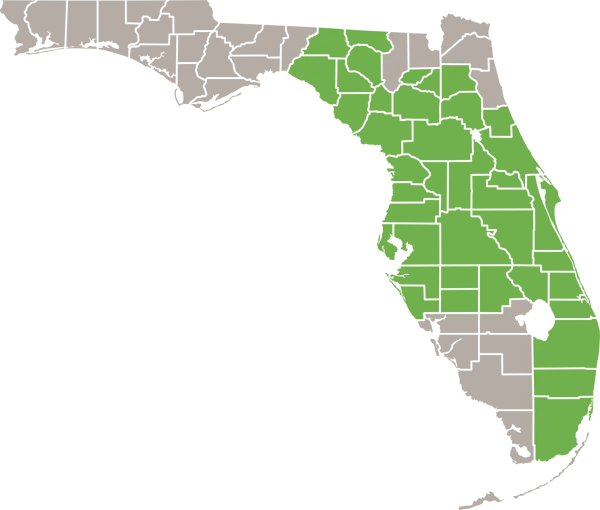
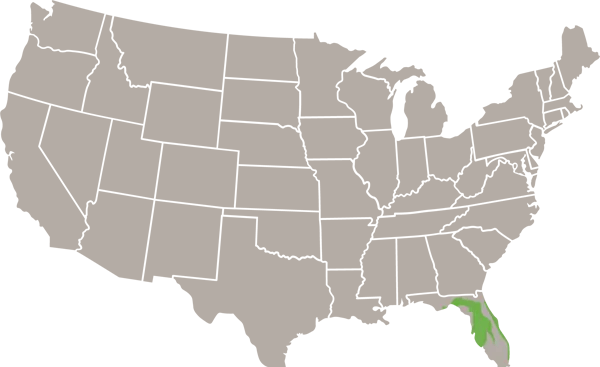
- Range
- Central Florida*
- Diet
- Seeds, Fruits, Insects
- Life Expectancy
- 1 Year
Quick Links
Florida Mice in Central Florida
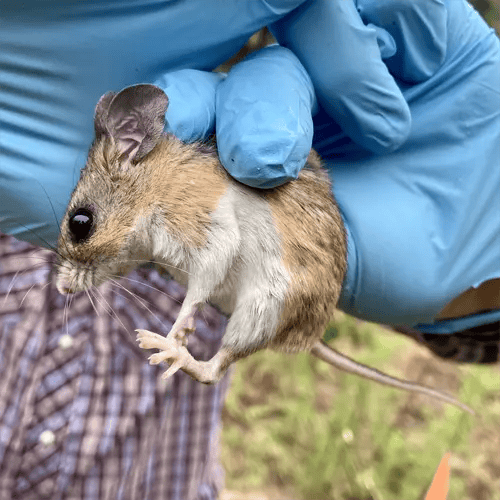
The Florida mouse (Podomys floridanus) is a small native rodent found throughout peninsular Florida. Often confused with the introduced house mouse (Mus musculus), the Florida mouse can be identified by its larger ears, grayish brown fur, and preference for wooded habitats.
This guide covers the biology, behavior, and control of Florida mice, an endemic rodent of conservation concern that also invades homes in central Florida seeking food and shelter
Appearance and Identification
The Florida mouse has characteristic features that distinguish it from similar looking house mice
Photo 256866114 (c) lparks713, CC BY-NC
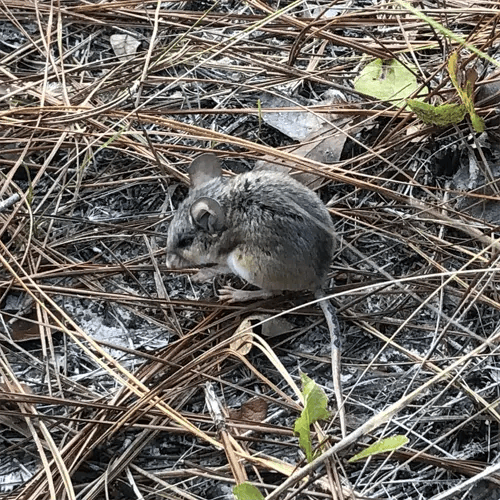
Adult Florida Water Rat
Juvenile Florida Water Rat
The introduced house mouse has smaller body size, ears, feet, and tail. House mice also have uniformly gray-brown fur without flecking from black guard hairs. Florida mice are found more often in natural habitats compared to the human-adapted house mouse.
Maturation Rate
Young Florida mice are sexually mature by 6 weeks old. Their average lifespan is about 1 year in the wild. Predation limits most Florida mice to just several months of life. Their high reproductive capacity allows rapid rebound after population declines.
Habits and Behavior
Florida mice are mostly nocturnal but may be active during daytime as well. They prefer wooded, shrubby areas but also invade garages, sheds, and homes. Florida mice are solitary and territorial, with home ranges of 0.1 to 0.25 acres (0.04 to 0.1 hectares).
Their nests are globular, 8 to 10 inches (20 to 25 cm) in diameter, and built either underground or under debris on the surface. Nests are lined with grasses, stems, Spanish moss, and shredded palmetto fronds. Florida mice occasionally climb but mostly forage on the ground, digging for seeds and insects.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Florida mice can breed year-round in central Florida. Females produce up to 7 litters annually with 1 to 7 young per litter. The gestation period is 23 days and the eyes open by 2 weeks old. Weaning occurs by 3 weeks of age
Ideal Habitat and Range
Central Florida’s warm, humid climate with abundant vegetation provides excellent habitat for Florida mice. Average temperatures are in the 70s°F (21-26°C) along with 50+ inches (1270+ mm) of annual rainfall.
Florida mice thrive in oak scrub forests, pine flatwoods, palm hammocks, and coastal scrub habitats. They also readily invade urban areas with overgrown vegetation, woodpiles, and palm trees. Plentiful cover and food allows Florida mice to flourish.
Diet and Feeding
Florida mice are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of plant and animal matter. Their diet consists primarily of:
- Seeds of native grasses, grains, berries, and fruits. This makes up the bulk of their diet.
- Acorns, hickory nuts, fungi such as lichens and mushrooms.
- Green vegetation including buds, leaves, moss, and algae.
- Insects such as beetles, caterpillars, ants, termites, and insect larvae.
- Snails, worms, and other invertebrates.
- Occasionally small vertebrates like bird eggs and nestlings.
While foraging primarily on the ground, Florida mice will readily climb to access nuts, fruits, and nests in vegetation. They locate food through scent, sound, and touch cues. Seeds and insects make up the majority of their diet, providing carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Florida mice obtain all the water they need from the foods they consume.


Common Health Risks
Although not major carriers of disease, Florida mice can potentially transmit:
- Hantavirus – Deer mice are the main carrier but Florida mice may spread. Causes serious lung disease.
- Lymphocytic choriomeningitis – Spread through saliva, urine, feces. Flu-like illness in humans.
- Rat bite fever – Bacteria in saliva can cause fever, joint pain, vomiting.
Florida mice may also contaminate food through feces and urine. Their shed hair and debris can trigger allergies and asthma symptoms in sensitive people. Exclusion and sanitation helps reduce health risks from Florida mouse infestations.
Preventing Florida Mouse Infestations
While Florida mice provide ecological benefits, they can sometimes enter homes by accident while foraging. The key is to exclude them from structures through proper proofing:
- Seal all potential entry points into the home larger than 1/4 inch (6 mm) using steel wool, copper mesh, caulk, or other durable materials. Pay close attention to areas where utilities enter the home.
- Trim back trees, shrubs, and vines so they do not touch or overhang the home’s exterior. Maintain at least a 3 foot (0.9 m) clearance.
- Eliminate woodpiles, debris piles, and dense vegetation close to the foundation that can provide shelter and access.
- Store human and pet food securely in chew-proof, sealed metal or plastic containers to deny access.
- Use baited snap traps or live traps as needed to remove any mice that find their way inside. Place traps along baseboards and potential entry points.
Through proactive proofing and exclusion, accidental home entry by Florida mice while foraging can be prevented. Their ecological benefits outweigh risks from occasional indoor exposure in homes.
Florida Mice in Central Florida – Conclusion
The Florida mouse is a unique native rodent of Florida scrub habitats that also readily invades homes. Their prolific breeding enables Florida mouse numbers to quickly rise if food and shelter is available.
Through exclusion, sanitation, and population control, Florida mice can be prevented and eliminated from structures. Trapping and sealing entry points are key, along with clearing brush and clutter near buildings.
With prompt action, Florida mice can be deterred before extensive damage or health risks arise in central Florida homes and businesses.