Evening Bat
- Scientific Name
- Nycticeius humeralis
- Also Known As
- North American Evening Bat
- Range
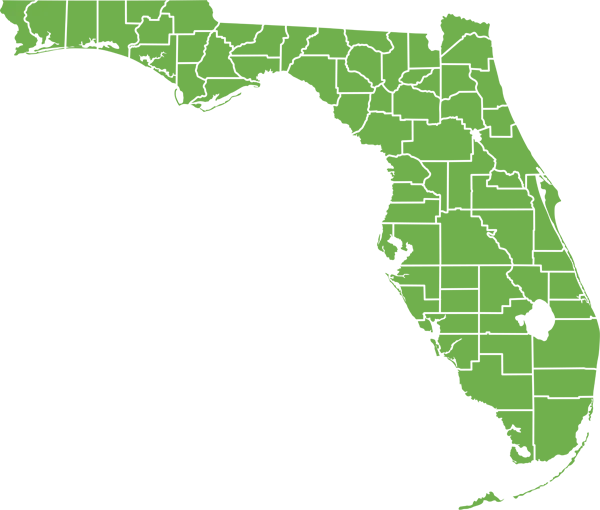
- All of Florida
- Diet
- Beetles, Moths, Flies, Winged Ants
- Life Expectancy
- 5 Years
Quick Links
The Evening Bat in Central Florida
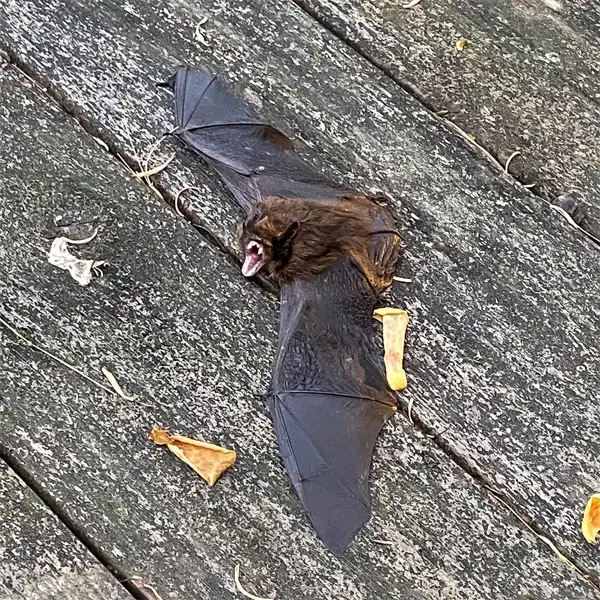
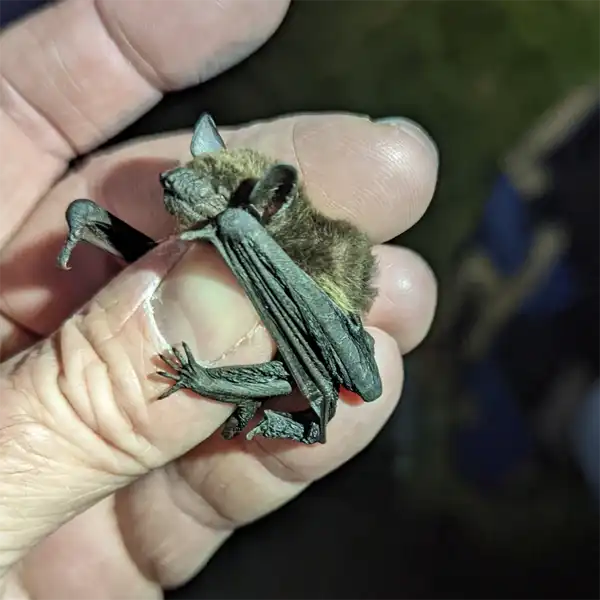
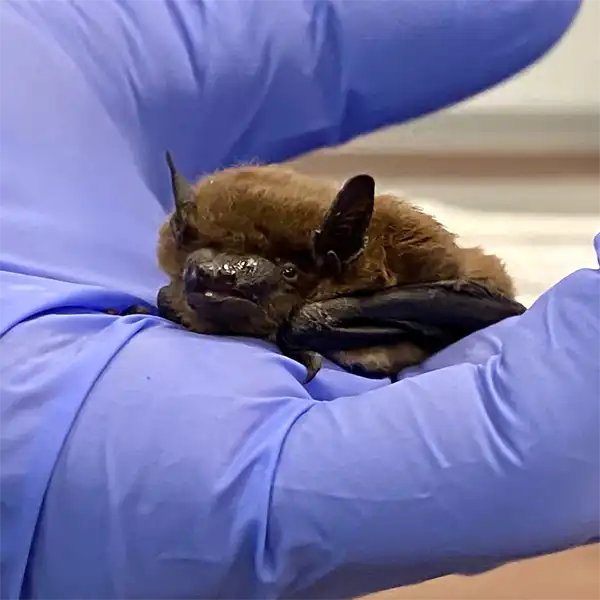
The evening bat (Nycticeius humeralis) is a small, insectivorous bat species found throughout the southeastern United States, including central Florida. As its name suggests, the evening bat is active at dusk and forages for insects at night. This guide provides identification tips, biology facts, potential health risks, and prevention methods for the evening bat in central Florida.
Appearance and Identification
The evening bat can be identified by the following physical characteristics in juveniles and adults
The evening bat can be distinguished from other Vespertilionidae bats by size, tricolored fur pattern, blunt tragus shape, and habit of roosting in foliage instead of buildings or caves.
Maturation Rate
Evening bat pups grow rapidly after birth, reaching full adult size by 20-30 days old. They are able to fly by 18-21 days. Weaning occurs by 3-4 weeks old. Sexual maturity is reached within the first year. The fast maturation enables evening bats to contribute to reproduction.
Habits and Behavior
The evening bat is aptly named for its early evening activity patterns. It emerges from roosts around dusk to forage. Evening bats have slow, maneuverable flight as they chase insects. This species uses echolocation calls to navigate and hunt within dense foliage.
Evening bats roost in the leaves of deciduous trees and shrubs. They are also found in Spanish moss. The bats change roosts frequently. These bats are migratory and travel south for winter. Evening bats hibernate in hollow trees or under loose bark. They are more solitary than colonial.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Female evening bats reach sexual maturity in their first year. Mating takes place in autumn. Females give birth to one pup per year in May-July. The gestation period is 60-90 days. Pups are weaned by 3-4 weeks old.
Ideal Habitat and Range
Central Florida’s humid, subtropical climate consists of warm to hot weather year-round, with rainy summers and drier winters. The average annual temperature ranges from 70-78°F. Rainfall measures 50-65 inches across the region annually.
These conditions allow dense vegetation like cypress swamps, oak hammocks, and pine forests to thrive. The abundant insect populations in these habitats provide nourishment for bats. Old, large trees supply roosting sites within the foliage or hollows. Evening bats migrate further south in winter when temperatures drop.
Overall, the warmer climate, plentiful insects, forests, and bodies of water in central Florida provide ideal roosting and feeding habitat for evening bats. These conditions allow sizable regional populations.
Diet and Feeding
Evening bats are insectivores, consuming a variety of flying insects each night. Their diet includes:
- Moths
- Beetles
- Flies
- Mosquitoes
- Mayflies
- Caddisflies
They hunt primarily by echolocation, emitting ultrasonic frequencies to detect prey while in flight. Evening bats can consume up to two-thirds of their body weight in insects nightly. They forage within forests and above water surfaces where flying insect activity is abundant.
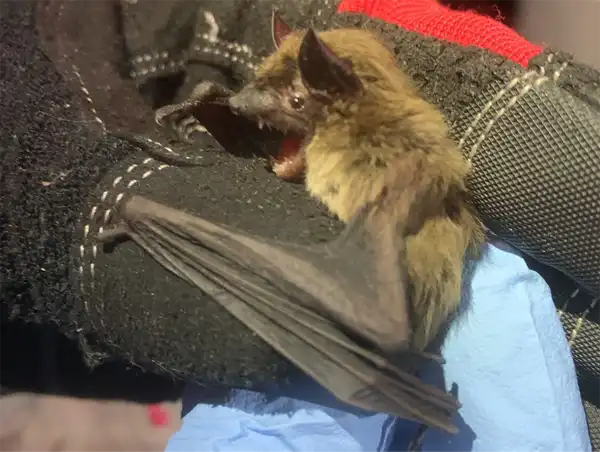
Photo 309553417 © macykrishnamoorthy, CC BY-NC

Common Health Risks
While overall public health risks are low, evening bats may occasionally transmit diseases like:
- Histoplasmosis – Caused by fungal spores from accumulated bat droppings in roosts. Can cause flu-like illness if inhaled.
- Rabies – Spread by infected saliva from bites. Fatal if left untreated. Evening bats only account for 1% of rabies cases.
- White-nose syndrome – Fungal disease harmful to hibernating bats. Humans cannot catch it.
The small size and foliage-roosting habits of evening bats make contact with people unlikely. Any sick bat should be avoided and reported to authorities for testing. Exclusion or removal of bats should only be done by licensed wildlife control professionals as bats are protected in Florida.
Preventing Evening Bat Encounters
While evening bats themselves don’t seek to invade homes, they may end up entering unintentionally if openings allow. To reduce unwanted encounters:
- Seal any openings or gaps greater than 1/4 inch in attics, roofs, walls, and chimneys using foam, hardware cloth, steel wool or caulk. This keeps bats from entering unintentionally.
- Ensure windows and doors close tightly with proper weatherstripping. Cover vent openings with fine mesh.
- Use ultrasound deterrents where appropriate to discourage bats from roosting on a property.
- Trim tree branches or shrubs back at least 3 feet from the house.
- Install bright outdoor lighting to keep insects away from the home.
- Use landscaping techniques to make the area less attractive to bats, such as removing standing water sources, reducing flowering plants, etc.
Evening Bats in Central Florida – Conclusion
In summary, the warm climate and natural habitats of central Florida support high populations of evening bats. While they play an important role in controlling insects, bats should not be allowed to roost or enter homes due to potential health and nuisance issues. Sealing up cracks, installing deterrents, and modifying landscaping can all help prevent undesirable bat encounters.
If a bat infestation does occur at a property, humane removal and exclusion by licensed wildlife experts is recommended. With preventative measures, homeowners can appreciate the benefits of bats safely and avoid issues associated with infestations.